____

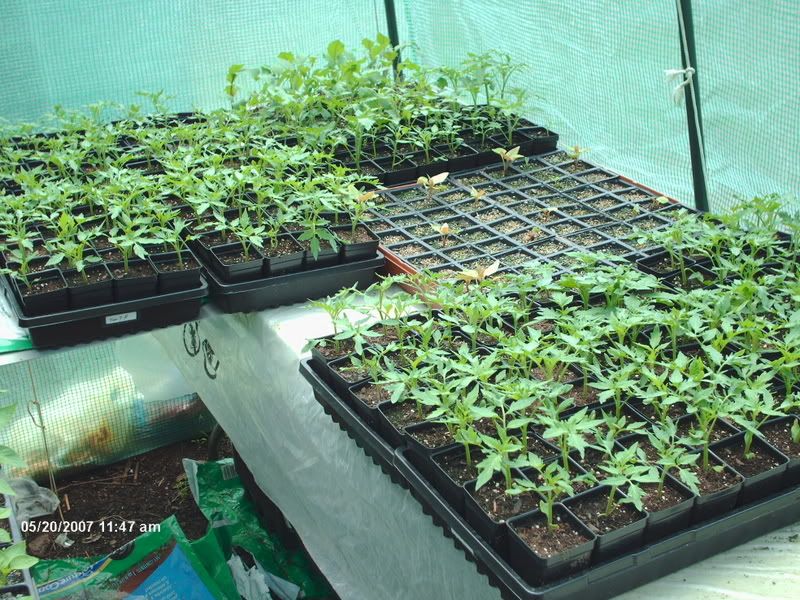
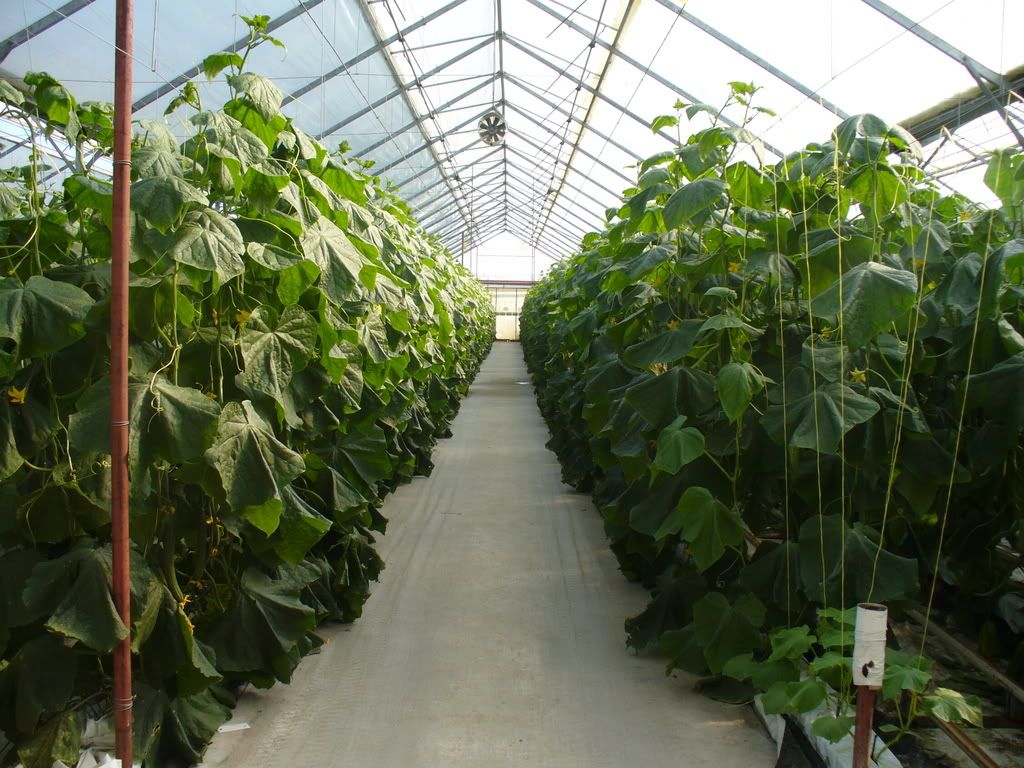
The two main types of hydroponics are solution culture and medium culture. Solution culture does not use a solid medium for the roots, just the nutrient solution. The three main types of solution culture are static solution culture, continuous flow solution culture, & aeroponics. The medium culture method has a solid medium for the roots and is named for the type of medium, e.g. sand culture, gravel culture or rockwool culture. There are two main variations for each medium, subirrigation and top irrigation. For all techniques, most hydroponic reservoirs are now built of plastic but other materials have been used including concrete, glass, metal, vegetable solids and wood. The containers should exclude light to prevent algae growth in the nutrient solution.


The two main types of hydroponics are solution culture and medium culture. Solution culture does not use a solid medium for the roots, just the nutrient solution. The three main types of solution culture are static solution culture, continuous flow solution culture, & aeroponics. The medium culture method has a solid medium for the roots and is named for the type of medium, e.g. sand culture, gravel culture or rockwool culture. There are two main variations for each medium, subirrigation and top irrigation. For all techniques, most hydroponic reservoirs are now built of plastic but other materials have been used including concrete, glass, metal, vegetable solids and wood. The containers should exclude light to prevent algae growth in the nutrient solution.
- Passive subirrigation/Fertigation -The medium generally has airy spaces for air circulation & allowing a oxygen to the roots and capillary action delivers water + nutrient solutions to the roots from the medium based. The simple model of this method normally has the container constantly sit in a shallow layer of nutrient solution or on a capillary mat saturated with nutrient solution. A variety of materials can be used for the medium: vermiculite, perlite, clay granules, rockwool, peat-moss, coco-peat or gravel. This method requires little maintenance and thus, the operational cost is quite low. It only requires only occasional refilling and replacement of the nutrient solution.
- Aeroponics is defined as a system where roots are continuously or discontinuously in an environment saturated with tiny nutrient drops (a mist or aerosol form). This method requires no substrate and entails growing plants with their roots suspended in a deep air or growth chamber with the roots periodically sprayed with a fine mist of oxygen rich, atomized nutrients. Excellent aeration and nutrient absorbtions is the main advantage of aeroponics.
- Deep Water Culture - The hydroponic method of plant production by means of suspending the plant roots in a solution of nutrient rich, oxygenated water. This methods favor the use of plastic buckets and large containers with the plant contained in a net pot suspended from the centre of the lid and the roots suspended in the nutrient solution.
- Organoponics is a hydroponic system converted to organic cultivation by replacing the inorganic fertilizer with organic compost. In a hydroponic system the roots need to be able to absorb nutrients as they touch the roots' capilaries. There is no soil for organic fertilizer to sit in and release nutrients.




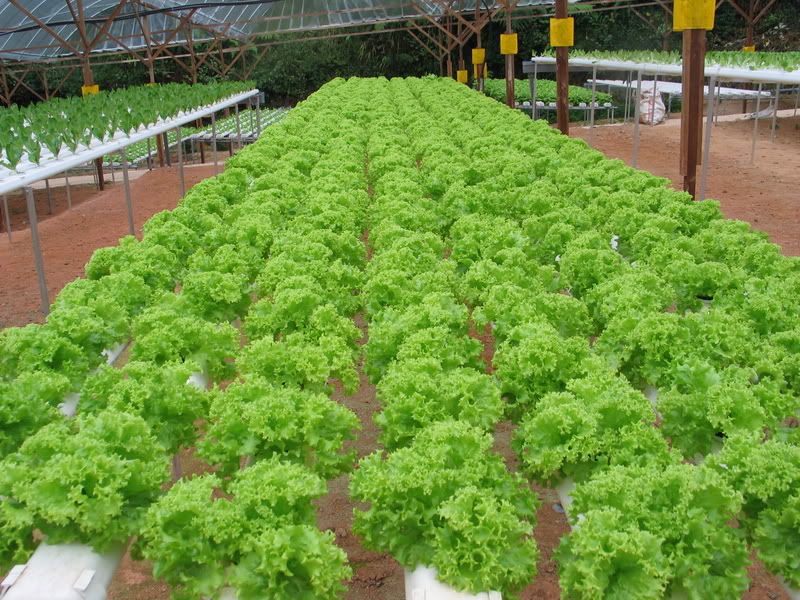
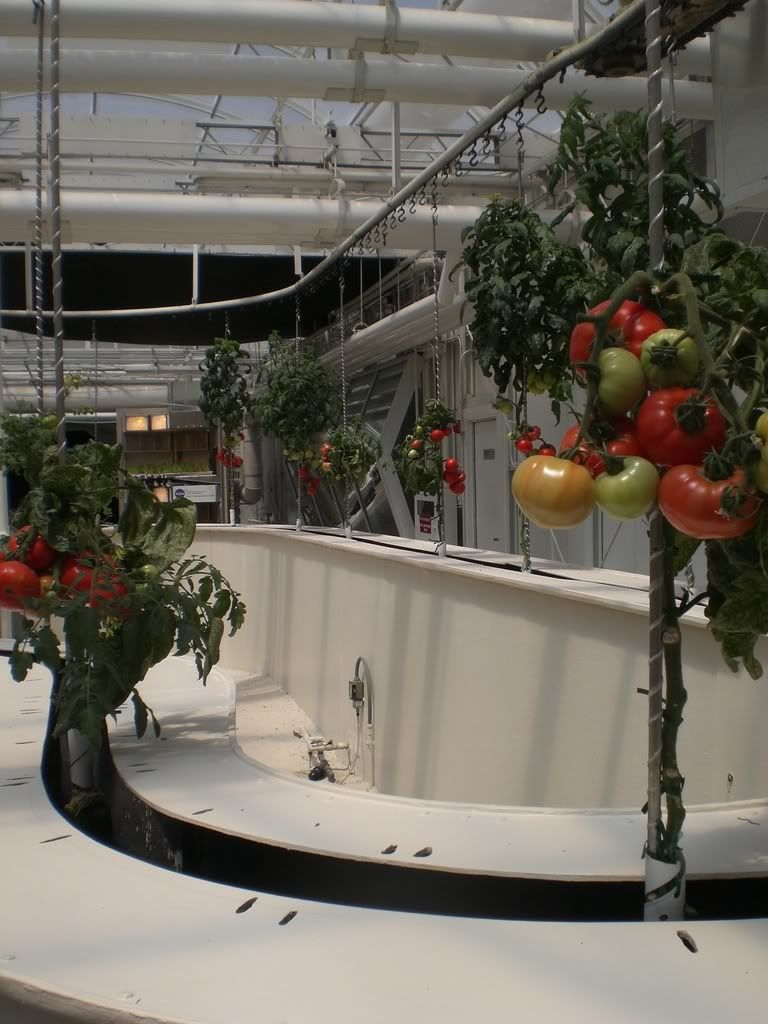
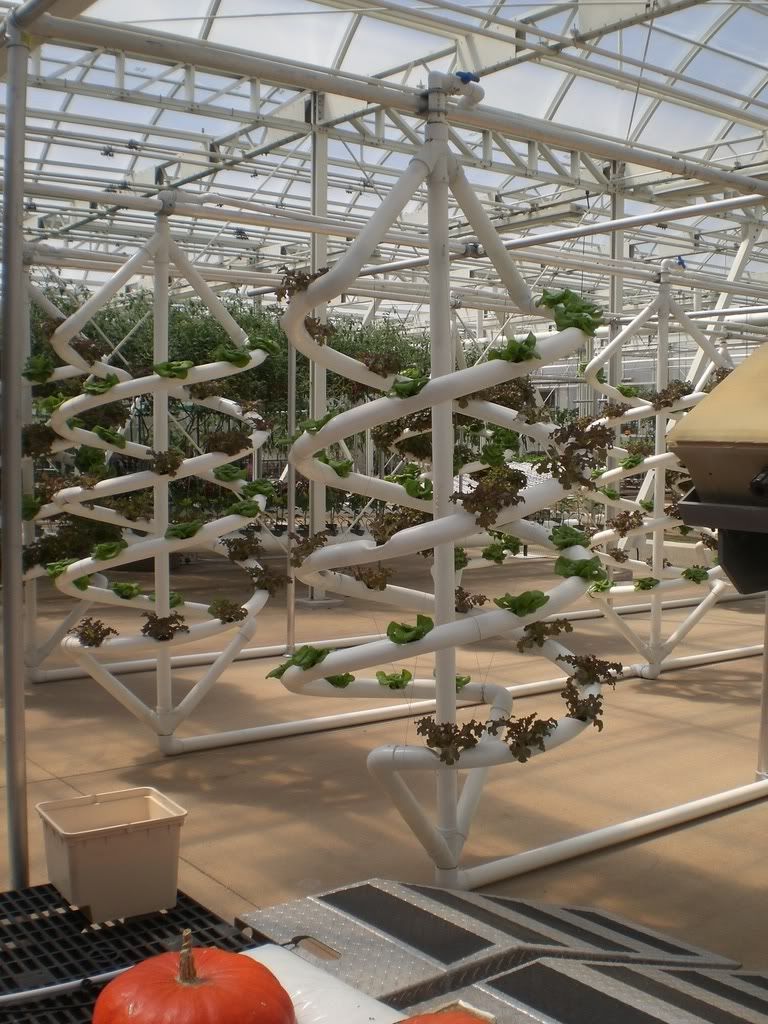
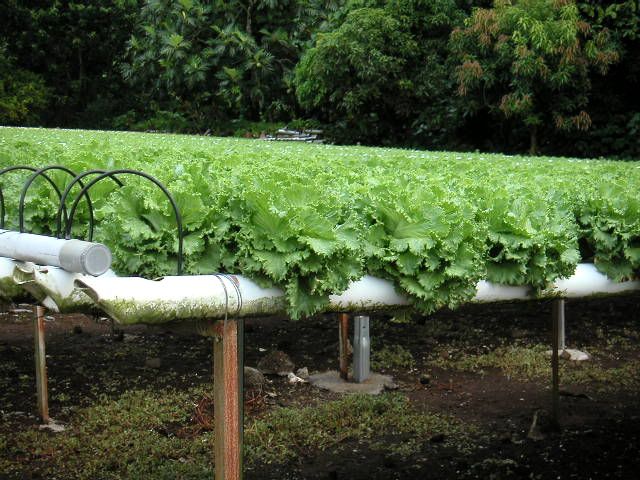
Models on many types of soilles culture or Hydroponic

























No comments:
Post a Comment