- Germination and post-emergence temperatures = 23-25 C (74-77 F)
- Production optimum temperatures = 22 C (72 F) day/20C (68 F) night.
- Conduction: diffusion of thermal energy through a continuous medium, the rate of which depends on the properties of the medium. Heat energy movement is always from a region of high temperature to lower temperature.
- Convection: diffusion of thermal energy between two dissimilar materials, usually between a gas and liquid, gas and solid, or liquid and solid. Heat energy movement is always from a region of high temperature to lower temperature.
- Radiation: radiation heat transfer occurs when electromagnetic energy leaves one object and is intercepted and absorbed by another. This differs markedly from conduction and convection. All objects emit radiation, warmer objects more so than cooler objects. The wavelengths usually considered to be involved in radiation heat transfer are in the infrared band.
Condensation: When the foliage of plants in the greenhouse are cooler than the surrounding air, moisture in the air may condense on the leaf surfaces. This is most common in the spring and fall when days are bright and warm and nights are cool and clear. The moisture that collects on the leaves serves as an ideal medium for the germination of several disease-causing spores, mainly powdery mildew. Condensation also occurs on the inside pf poly-covered greenhouse when the inside air is warm and humid and the outside air is cold. Under these conditions, condensation can rain-down on the foliage creating an environment for diseases.
Greenhouses heat up during the day for two reasons: 1) the greenhouse effect, 2) because the greenhouse is an enclosed space. How much a greenhouse heat up during the day depends on how much solar radiant energy is coming in through the glazing, what happens to that energy, and how much is retained.
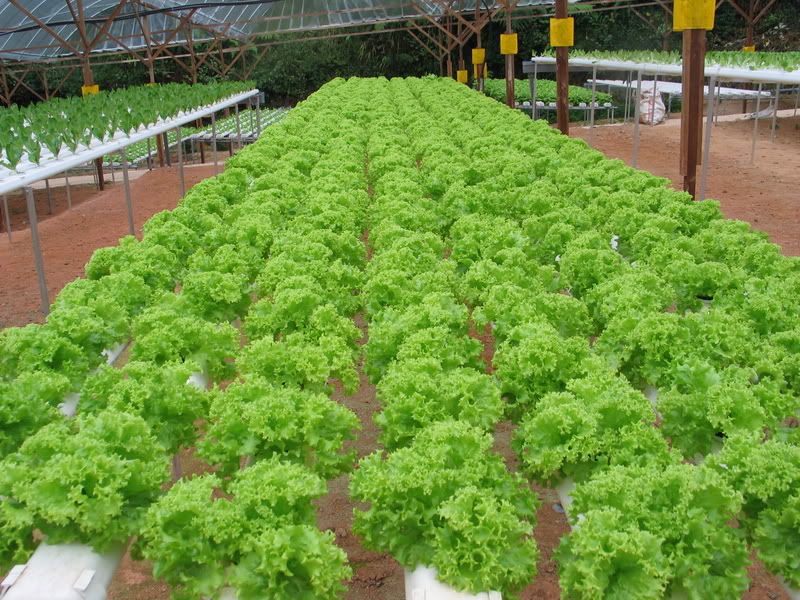
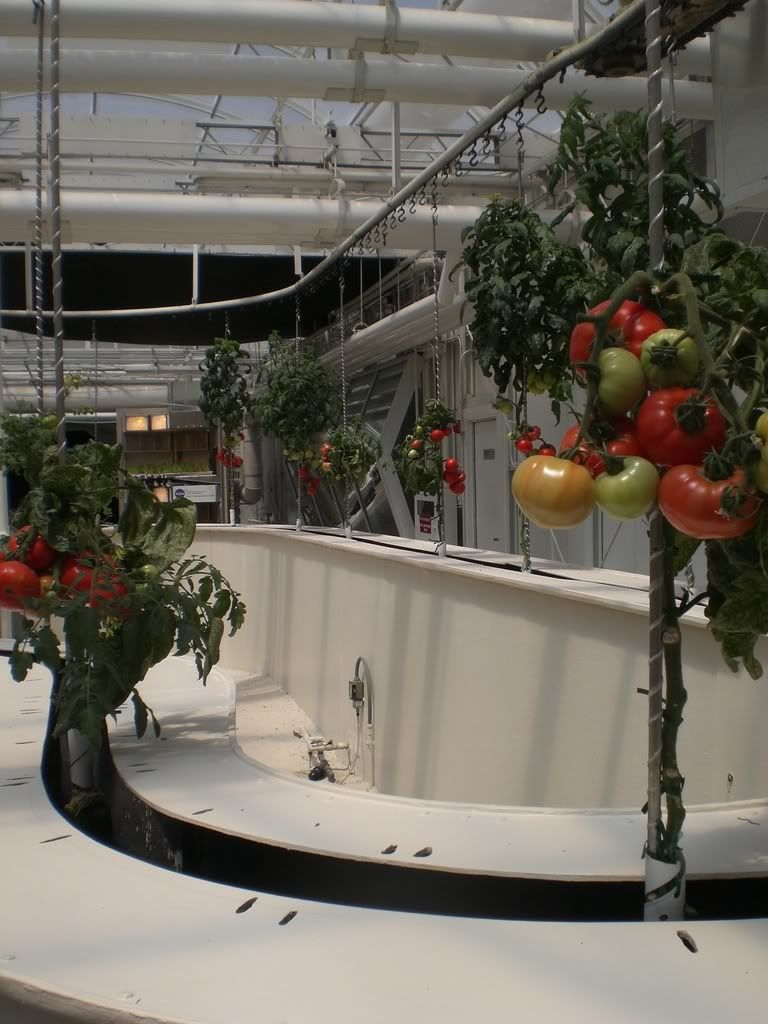
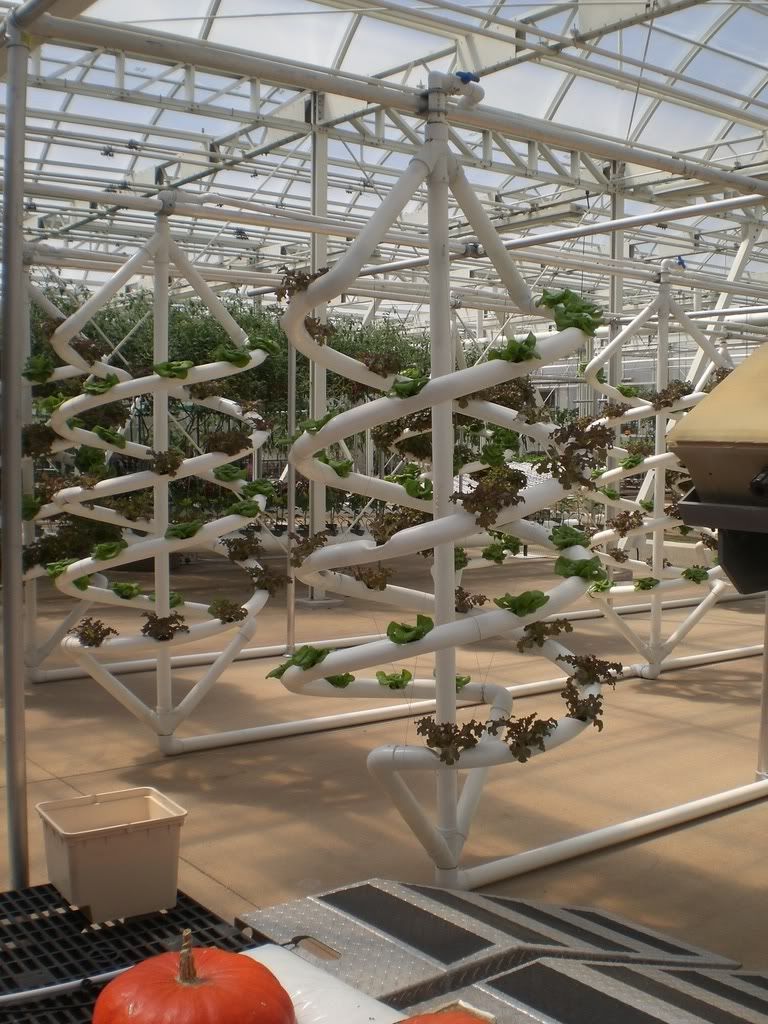
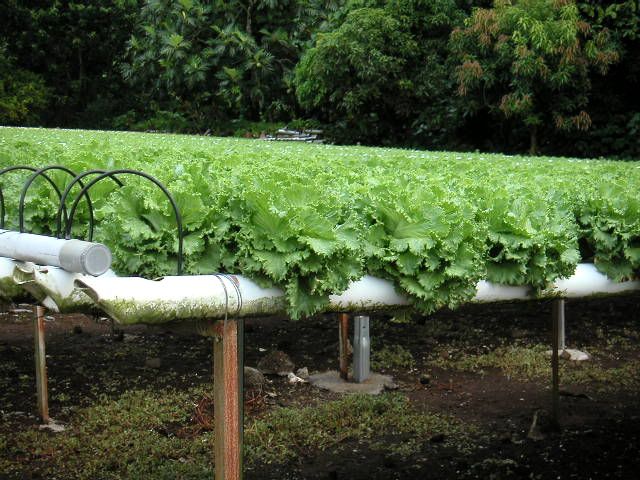

























No comments:
Post a Comment