R NUTRIENT DELIVERY SYSTEMS
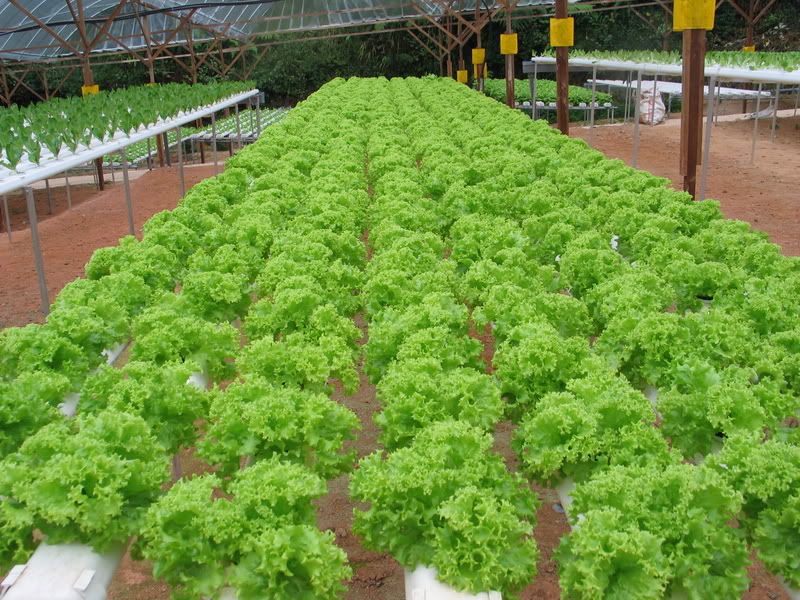
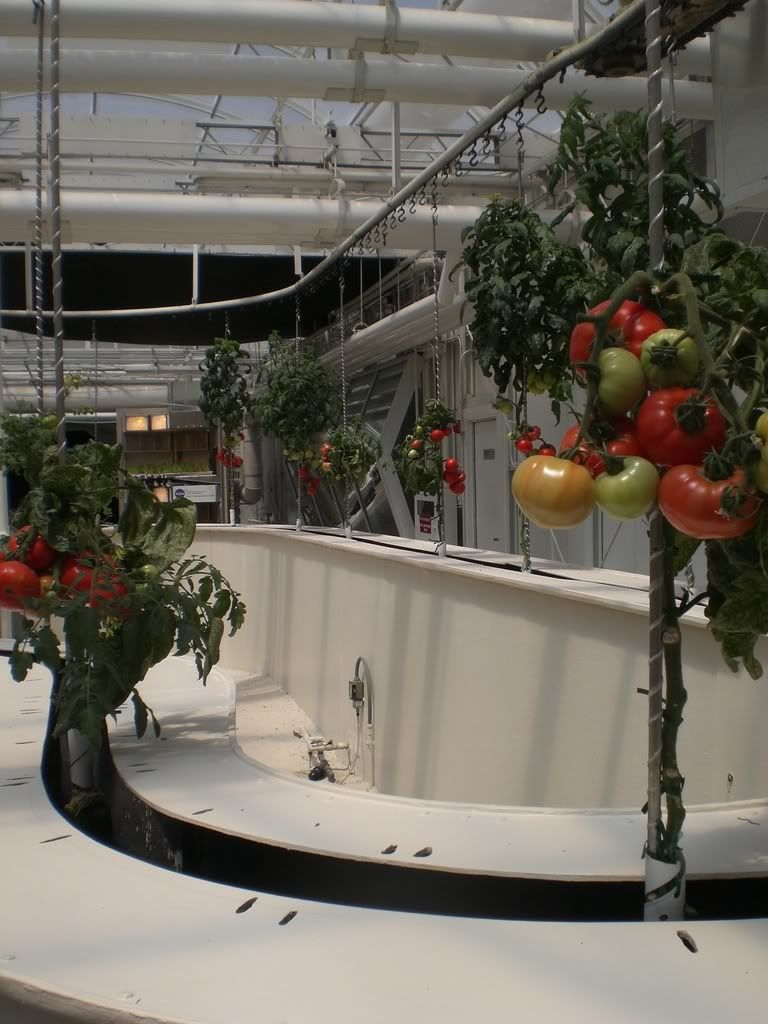
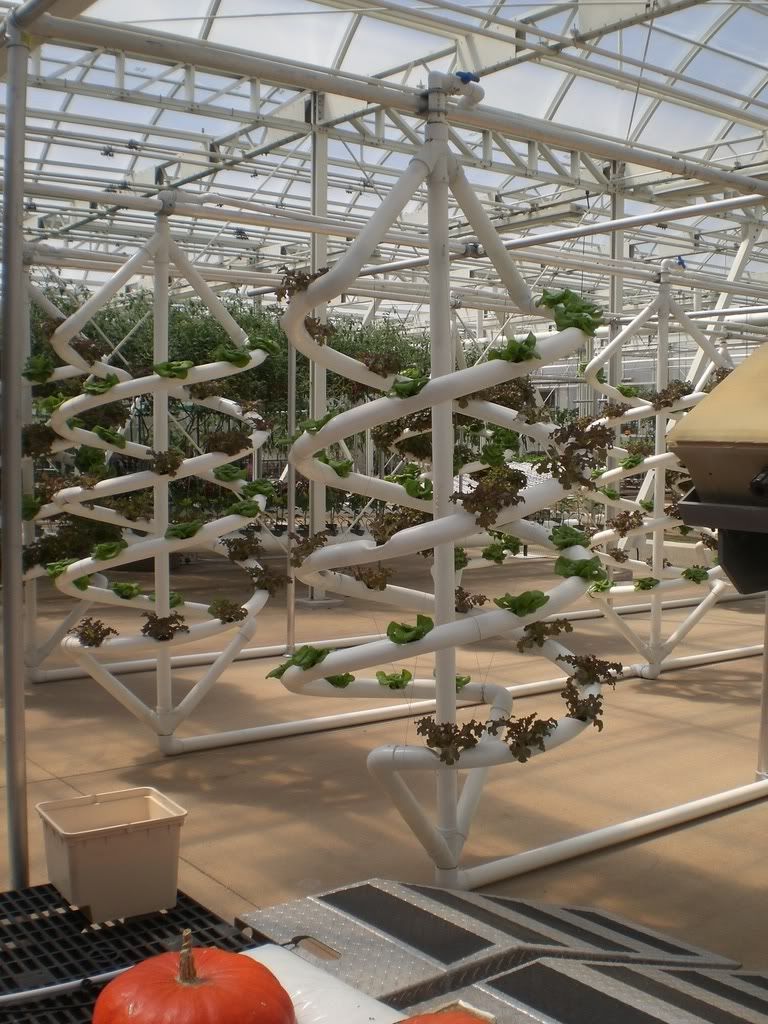
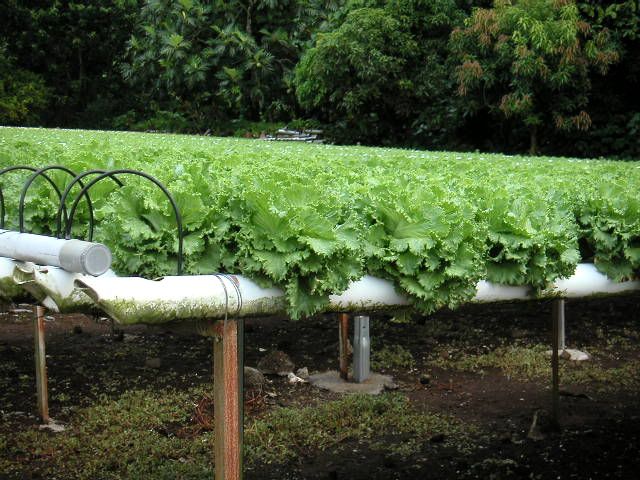
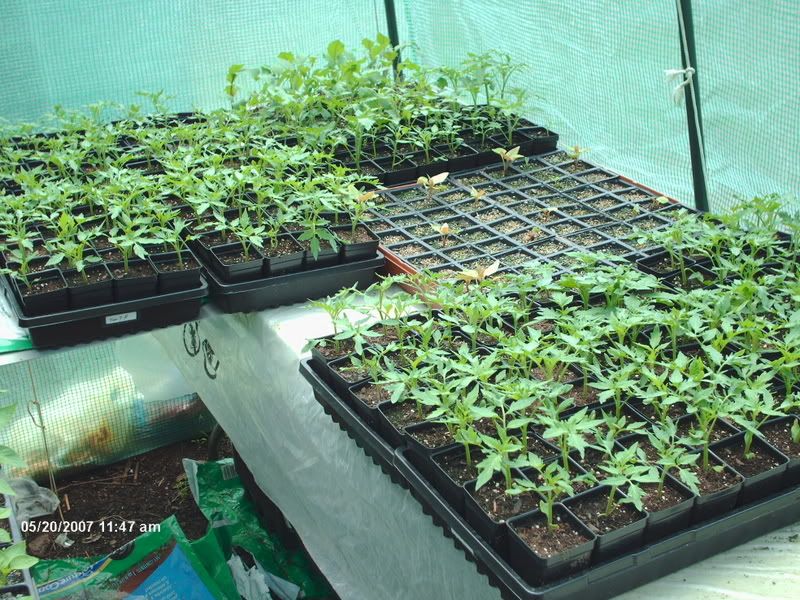
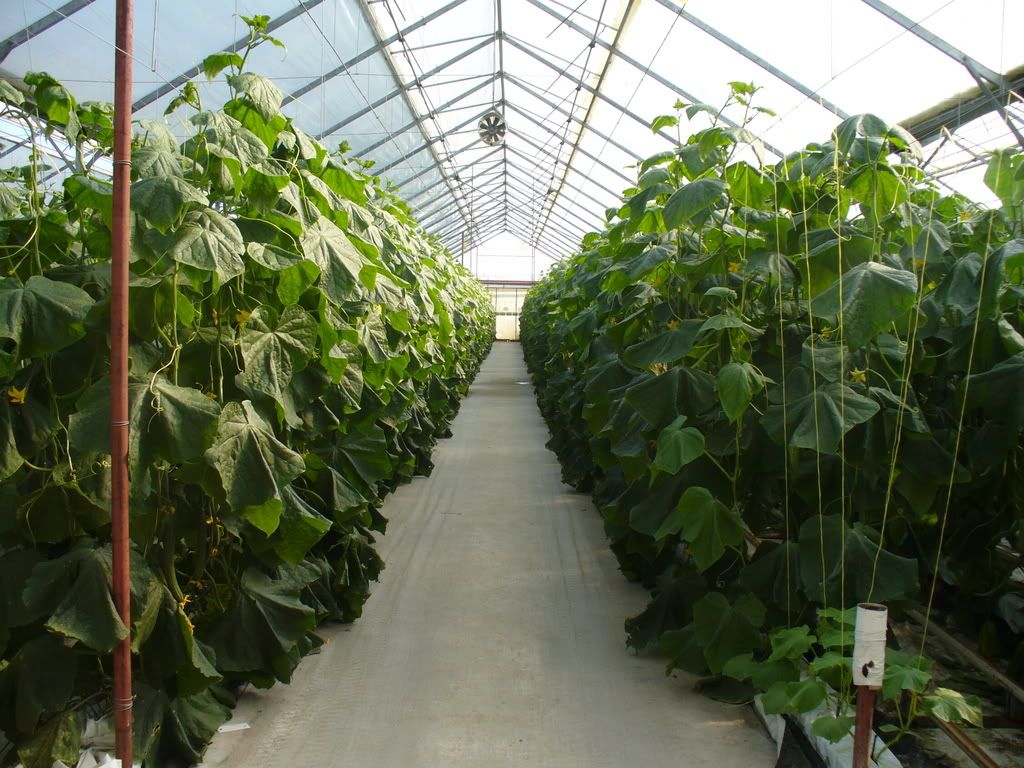
- Simple systems: Non-recirculating/air gap system or the raft system where the roots hang down directly into the nutrient solution. Basic wick system in which the nutrient solution is drawn up by an absorbent wick into an aggregate where the roots grow.
- Complex systems: The flood and drain, top feeder, NFT or Aeroponic systems all of which require pumps to move the nutrient solution from a reservoir or series of tanks to the plants via PVC, poly and drip tubing, emitters, etc.
- If [H] = 10-7, then pH = 7 (Neutral)
- If [H] = 10-4, then pH = 4 (Acidic)
- If [H] = 10-9, then pH = 9 (Basic)
Ways to test the pH: Litmus paper (color change), pH meter (analog or digital)- meas. [H+]
For most plants: pH 5 – 7. For tomatoes: 5.8 – 6.3. Above pH 7 may cause problems with nutrient uptake. Below pH 5 may cause abnormal absorption of certain ions resulting in deficiencies or toxicities.
2) EC (Electrical conductivity): a measure of the total salts in water. Pure water (no salts) does not conduct electricity: EC = 0. The higher the salt levels, the higher the EC. Measured in: mS/cm (milli-Siemens per centimeter)
3) TDS (total dissolved solids): For tomatoes: EC = 2.5 – 3.5 mS/cm (depends on light, plant architecture desired, etc.)
Elevated salt levels: Certain geographic areas have high salt levels in the water :
- High boron, fluoride, chloride, sulfates and sodium: -Can cause poor plant growth. -May influence soluble salt levels in the water.
- High iron, especially in “hard water” (having high Ca and Mg): -Can cause rusty spots on leaves with overhead irrigation.
- High salt levels can also cause rapid salt buildup on cooling pads. -May need to bleed off and replace pad water regularly.

























1 comment:
DRIP IRRIGATION, INTEGRATED DRIP LINES, INLINE LATERAL PIPES, DRIP EMITTERS, FERTIGATION, DRIP IRRIGATION MANUFACTURERS INDIA, INTEGRATED DRIP LINES MANUFACTURERS INDIA, INLINE LATERAL PIPES MANUFACTURERS INDIA, DRIP EMITTERS MANUFACTURERS INDIA, FERTIGATION MANUFACTURERS INDIA
Post a Comment